publications
2025
-
 Beyond Canes and Guide Dogs: A Review of 40 Years of Robotics for Wayfinding, Navigating, and Orienting Assistance for People with Visual ImpairmentsJohn Pohovey, Maria Lusardi, Aamir Hasan, and 5 more authorsAug 2025
Beyond Canes and Guide Dogs: A Review of 40 Years of Robotics for Wayfinding, Navigating, and Orienting Assistance for People with Visual ImpairmentsJohn Pohovey, Maria Lusardi, Aamir Hasan, and 5 more authorsAug 2025Robotic aids that enrich the lives of Persons with Visual Impairments (PwVI) are becoming increasingly popular. Their development is motivated by the significant navigational challenges faced by PwVI that negatively impacts their independence and quality of life. Additionally, traditional tools such as white canes, guide dogs, and tactile maps, although useful, lack the adaptability and situational awareness that robots offer. This survey presents the first comprehensive review of robotic solutions for wayfinding, spanning over 150 works in the past 40 years. We propose unifying definitions wayfinding and robotic wayfinding across fields including robotics, human factors, urban theory, and several other social sciences in the context of assistive robotics technologies for PwVI, and provide rigorous classification along axes of embodiment, communication, sensing, and user evaluation. Informed by the gaps in the literature, we provide critical analysis and explanation into six research questions spanning from factors in device design trends, evolutions of unidirectional and bidirectional communication mediums, and robustness of system evaluations and user studies. Furthermore, we analyze and compare state-of-the-art approaches spanning human-robot interaction, advanced perception pipelines, and experimental design. We identify limitations and open challenges for developing robotic wayfinding solutions and outline recommendations for future research directions. The full annotated dataset and detailed taxonomy for all surveyed papers are released in the Inter-university Consortium for Political and Social Research (ICPSR) repository https://doi.org/10.3886/E235425V1 .
@misc{pohovey2025beyondcanes, title = {Beyond Canes and Guide Dogs: A Review of 40 Years of Robotics for Wayfinding, Navigating, and Orienting Assistance for People with Visual Impairments}, author = {Pohovey, John and Lusardi, Maria and Hasan, Aamir and Liu, Shuijing and Schreiber, Andre and Olatunji, Samuel A. and Rogers, Wendy A. and Driggs-Campbell, Katherine}, year = {2025}, month = aug, publisher = {Open Engineering Inc}, eprint = {https://engrxiv.org/preprint/view/4985/8501}, archiveprefix = {engrXiv}, primaryclass = {}, doi = {10.31224/4985}, }
2024
-
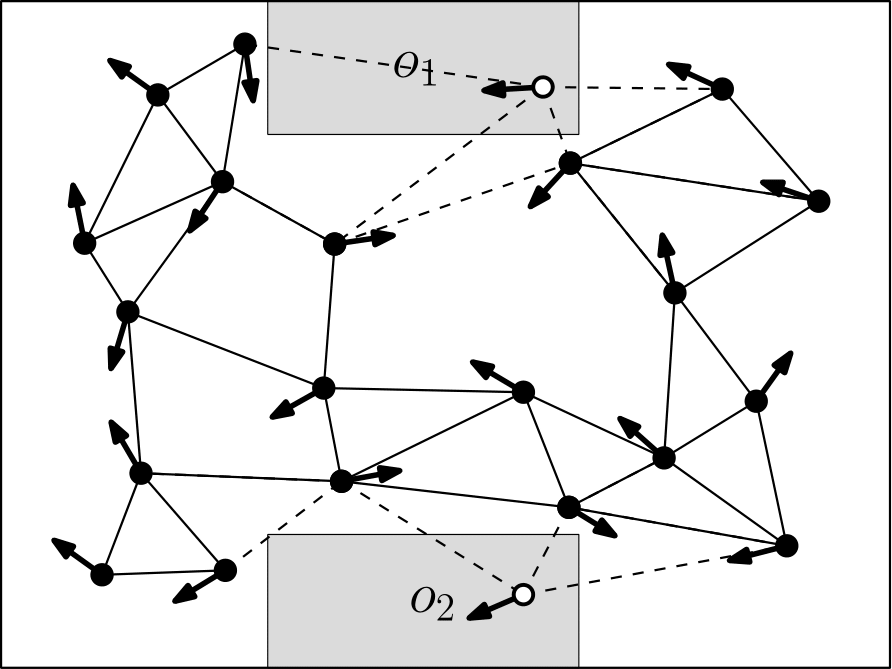 SPITE: Simple Polyhedral Intersection Techniques for modified EnvironmentsStav Ashur, Maria Lusardi, Marta Markowicz, and 4 more authorsAug 2024
SPITE: Simple Polyhedral Intersection Techniques for modified EnvironmentsStav Ashur, Maria Lusardi, Marta Markowicz, and 4 more authorsAug 2024Motion planning in modified environments is a challenging task, as it compounds the innate difficulty of the motion planning problem with a changing environment. This renders some algorithmic methods such as probabilistic roadmaps less viable, as nodes and edges may become invalid as a result of these changes. In this paper, we present a method of transforming any configuration space graph, such as a roadmap, to a dynamic data structure capable of updating the validity of its nodes and edges in response to discrete changes in obstacle positions. We use methods from computational geometry to compute 3D swept volume approximations of configuration space points and curves to achieve 10-40 percent faster updates and up to 60 percent faster motion planning queries than previous algorithms while requiring a significantly shorter pre-processing phase, requiring minutes instead of hours needed by the competing method to achieve somewhat similar update times.
@misc{spite24, author = {Ashur, Stav and Lusardi, Maria and Markowicz, Marta and Motes, James and Morales, Marco and Har-Peled, Sariel and Amato, Nancy M.}, title = {SPITE: Simple Polyhedral Intersection Techniques for modified Environments}, year = {2024}, eprint = {2407.00259}, archiveprefix = {arXiv}, primaryclass = {cs.RO}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.00259}, } - Dependable Spanners via Unreliable EdgesSariel Har-Peled, and Maria C. LusardiAug 2024
Let P be a set of n points in ℝd, and let ε,ψ∈(0,1) be parameters. Here, we consider the task of constructing a (1+ε)-spanner for P, where every edge might fail (independently) with probability 1−ψ. For example, for ψ=0.1, about 90% of the edges of the graph fail. Nevertheless, we show how to construct a spanner that survives such a catastrophe with near linear number of edges. The measure of reliability of the graph constructed is how many pairs of vertices lose (1+ε)-connectivity. Surprisingly, despite the spanner constructed being of near linear size, the number of failed pairs is close to the number of failed pairs if the underlying graph was a clique. Specifically, we show how to construct such an exact dependable spanner in one dimension of size O(nψlogn), which is optimal. Next, we build an (1+ε)-spanners for a set P⊆ℝd of n points, of size O(Cnlogn), where C≈1/(εdψ4/3). Surprisingly, these new spanners also have the property that almost all pairs of vertices have a ≤4-hop paths between them realizing this short path.
@misc{spanners24, title = {Dependable Spanners via Unreliable Edges}, author = {Har-Peled, Sariel and Lusardi, Maria C.}, year = {2024}, eprint = {2407.01466}, archiveprefix = {arXiv}, primaryclass = {cs.CG}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.01466}, }
2021
-
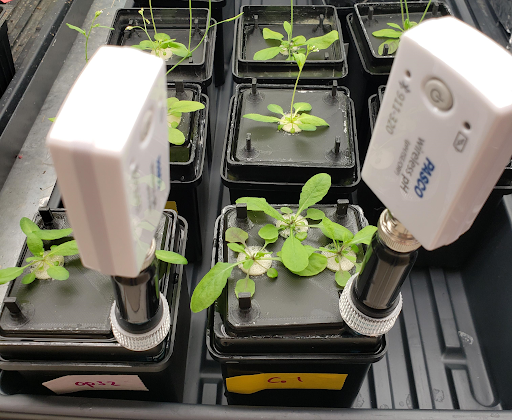 Development of automated sensors to track pH changes elicited by iron deficiency in hydroponic culturesMaria Clare Lusardi, Emily Walter, Dario Alavez, and 1 more authorIn , Aug 2021
Development of automated sensors to track pH changes elicited by iron deficiency in hydroponic culturesMaria Clare Lusardi, Emily Walter, Dario Alavez, and 1 more authorIn , Aug 2021Iron (Fe) is an essential nutrient for plant growth, and plants are the main source of Fe for humans and livestock. The World Health Organization estimates that Fe deficiency affects 30% of the world’s population and is considered the most prevalent nutritional deficiency around the globe. Thus, understanding the molecular mechanisms that plants use to accumulate Fe will allow the development of biofortified crops for better human nutrition. Despite recent and significant advances in our understanding of how plants respond to Fe deficiency, the molecular and physiological mechanisms behind Fe deficiency are still poorly understood. This is due in part to the static nature of how our field currently assesses Fe deficiency responses. For instance, plants are known to acidify the root environment to make Fe more available but currently, data describing the timing and progression of this acidification is lacking. To solve this issue, we developed an automated pH tracking system to monitor pH changes in hydroponic systems. As a proof of concept, we tracked the acidification of media on maize plants grown over a week with and without Fe. We also compared the accuracy and consistency of two different sensors, PASCO’s ready-to-use Wireless pH Sensor and DFRobot’s DIY open-source Gravity pH Meter Pro. Overall, the PASCO sensors showed more consistent readings and required minimal software and hardware setup. DFRobot sensors on the other hand showed much more variance in their readings and required a microcontroller, a Raspberry Pi, and self-written software to read and analyze the values. However, the open-source capacity allows more possibilities for future development, such as real-time data uploads. Further experiments will focus on optimizing the sensitivity of both systems to provide an informed data-driven comparison of each sensor brand.
@inproceedings{bips21, author = {Lusardi, Maria Clare and Walter, Emily and Alavez, Dario and Mendoza Cozatl, David}, title = {Development of automated sensors to track pH changes elicited by iron deficiency in hydroponic cultures}, year = {2021}, keywords = {pH;hydroponics;iron deficiency;automated sensors}, }
2020
-
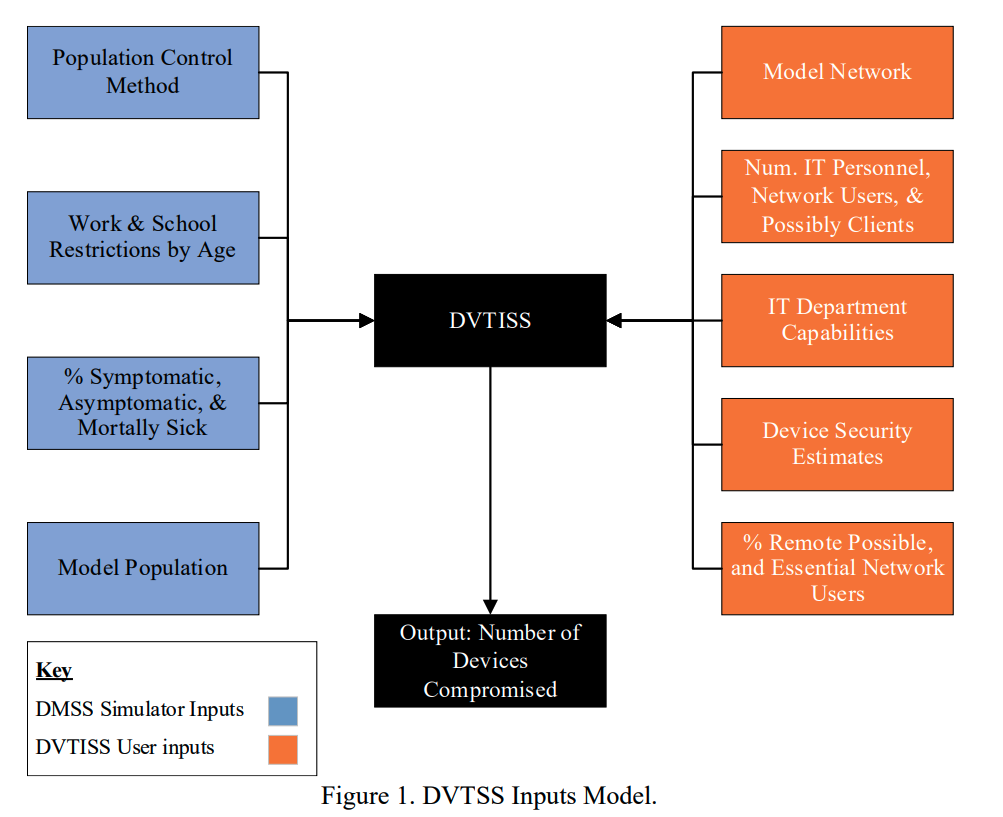 Determining the Impact of Cybersecurity Failures During and Attributable to Pandemics and Other Emergency SituationsMaria Clare Lusardi, Isaac Dubovoy, and Jeremy StraubIn 2020 IEEE Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop (AIPR) , Aug 2020
Determining the Impact of Cybersecurity Failures During and Attributable to Pandemics and Other Emergency SituationsMaria Clare Lusardi, Isaac Dubovoy, and Jeremy StraubIn 2020 IEEE Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop (AIPR) , Aug 2020In emergency situations, such as the current COVID-19 pandemic, less immediate concerns such as cybersecurity and long-term economic impact can fall by the wayside. This paper presents a discussion of the impact of cybersecurity issues that occur during and are attributable to pandemics and other emergency situations. This discussion is facilitated by a simulation tool, the Disaster Vulnerability Threat and Impact Simulator System (DVTISS). DVTISS simulates the network structure, security measures, user characteristics and demographics, data, and devices of an organization or region’s computing infrastructure. The system is provided input parameters and performs analysis to identify the combined results of numerous different decisions, which are made in concert, to identify the types of vulnerabilities that may be present and the impact of their exploitation. The impacts of system unavailability are considered. This can aid businesses, governments and others in determining the level of prioritization that should be given to cybersecurity considerations. The simulator can also be used for disaster preparedness and planning, evaluating particular response strategies and the evaluation of laws and policies that impact IT decision making during emergencies. This paper uses the DVTISS tool to consider organizational responses to several example emergency situations. It demonstrates the utility of the tool as well as its efficacy for decision making support. Based on the example emergencies, the paper also discusses key areas of vulnerability during emergency situations and their financial, data and system outage impacts.
@inproceedings{reu20, author = {Lusardi, Maria Clare and Dubovoy, Isaac and Straub, Jeremy}, booktitle = {2020 IEEE Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop (AIPR)}, title = {Determining the Impact of Cybersecurity Failures During and Attributable to Pandemics and Other Emergency Situations}, year = {2020}, pages = {1-6}, keywords = {Economics;COVID-19;Performance evaluation;Pandemics;Decision making;Tools;Planning;pandemic;cybersecurity;simulator;economics;policy}, doi = {10.1109/AIPR50011.2020.9425225}, publisher = {IEEE}, }